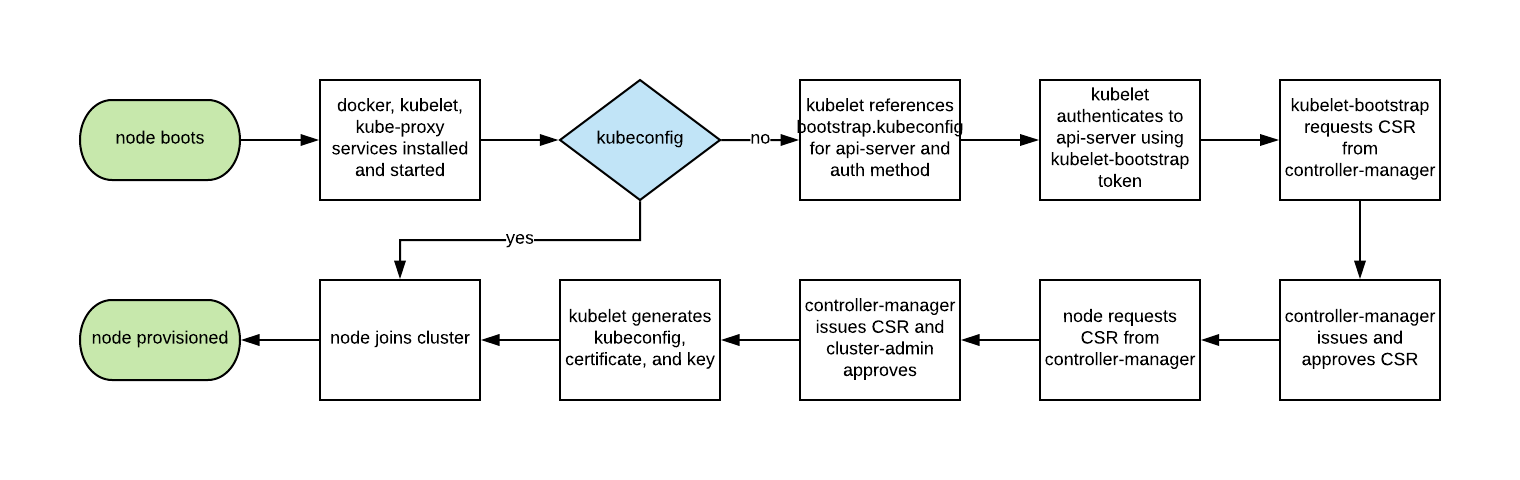
TLS bootstrapping with token file
Workflow
Create a Token
$ head -c 16 /dev/urandom | od -An -t x | tr -d ' 'Output
12c12e7eb3a9c3f9255bb74529c6768e$ echo 12c12e7eb3a9c3f9255bb74529c6768e,kubelet-bootstrap,10001,\"system:bootstrappers\" |sudo tee -a /etc/kubernetes/config/bootstrap-token.conf12c12e7eb3a9c3f9255bb74529c6768e,kubelet-bootstrap,10001,"system:bootstrappers"Create a token auth file
$ cat /etc/kubernetes/config/bootstrap-token.conf12c12e7eb3a9c3f9255bb74529c6768e,kubelet-bootstrap,10001,"system:bootstrappers"Add below flags to API server
--enable-bootstrap-token-auth=true \
--token-auth-file=/etc/kubernetes/config/bootstrap-token.conf \Add RBAC for Node TLS bootstrapping and certificate auto renewal.
cat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: create-csrs-for-bootstrapping
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:bootstrappers
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:node-bootstrapper
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
EOFcat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: auto-approve-csrs-for-group
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:bootstrappers
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:nodeclient
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
EOFcat <<EOF | kubectl create -f -
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
metadata:
name: auto-approve-renewals-for-nodes
subjects:
- kind: Group
name: system:nodes
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
roleRef:
kind: ClusterRole
name: system:certificates.k8s.io:certificatesigningrequests:selfnodeclient
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
EOFCreate a bootstrap-kubeconfig which can be used by kubelet
TOKEN=$(awk -F "," '{print $1}' /etc/kubernetes/config/bootstrap-token.conf)
KUBERNETES_PUBLIC_ADDRESS=$(grep master /etc/hosts |awk '{print $1}')kubectl config --kubeconfig=bootstrap-kubeconfig set-cluster bootstrap --embed-certs=true --server=https://${KUBERNETES_PUBLIC_ADDRESS}:6443 --certificate-authority=ca.pemkubectl config --kubeconfig=bootstrap-kubeconfig set-credentials kubelet-bootstrap --token=${TOKEN}kubectl config --kubeconfig=bootstrap-kubeconfig set-context bootstrap --user=kubelet-bootstrap --cluster=bootstrapkubectl config --kubeconfig=bootstrap-kubeconfig use-context bootstrapCopy bootstrap-kubeconfig to worker node
Kubelet configuration
- Turnoff swap
$ sudo swapoff /dev/dm-1 ##<--- select appropriate swap device based on your OS configInstall and start docker service
Once docker is installed , execute below steps to make docker ready for
kubeletintegration.
$ sudo vi /lib/systemd/system/docker.service- Disable iptables, default bridge network and masquerading on docker
ExecStart=/usr/bin/dockerd -H fd:// --bridge=none --iptables=false --ip-masq=false- Cleanup all docker specific networking from worker nodes
$ sudo iptables -t nat -F
$ sudo ip link set docker0 down
$ sudo ip link delete docker0- Restart docker
$ sudo systemctl restart docker- Move bootstrap config file to
/var/lib/kubelet/
$ mkdir /var/lib/kubelet/
$ sudo mv bootstrap-kubeconfig /var/lib/kubelet/ $ cat <<EOF |sudo tee /etc/systemd/system/kubelet.service
[Unit]
Description=Kubernetes Kubelet
Documentation=https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes
After=containerd.service
Requires=containerd.service
[Service]
ExecStart=/usr/local/bin/kubelet \
--bootstrap-kubeconfig=/var/lib/kubelet/bootstrap-kubeconfig \
--cert-dir=/var/lib/kubelet/ \
--kubeconfig=/var/lib/kubelet/kubeconfig \
--rotate-certificates=true \
--runtime-cgroups=/systemd/system.slice \
--kubelet-cgroups=/systemd/system.slice
Restart=on-failure
RestartSec=5
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
EOF- Reload and start the kubelet service
$ sudo systemctl daemon-reload
$ sudo systemctl start kubeletNow execute kubectl get nodes and see if the node is listed there.
You may configure kube-proxy as a DaemonSet so that it will automatically start after node registration completion.